Guide
This text is machine translated.
Sensors: Useful little helpers in industry, research or everyday life
Sensors are hardly indispensable for industry and research, as well as for our everyday life. They collect data that can be collected and evaluated using instrumentation. The variety of sensors is extremely large. You can find out which types of sensors are available and how they work in our guide.
What was a
What was the sensor?
Measuring principles of sensors
Application areas of sensors
Our practical tip: Integrate a software
FAQ - Frequently Asked Questions about Sensors
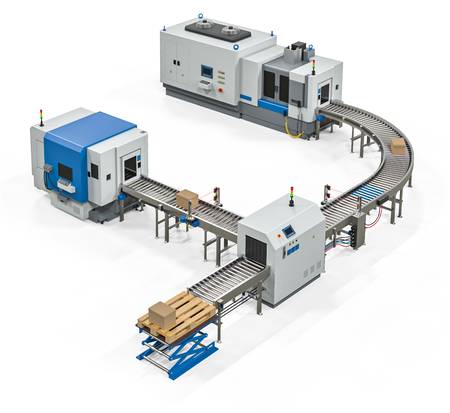

Application example from the field & process technology
What was a

Whether in thermometers, surveillance cameras, smoke detectors, blood pressure monitors or heaters – sensors meet us almost everywhere in everyday life. The term "sensor" derives from the Latin verb sentire and means as much as "observe", "perceive", "feel". The task of a sensor can be illustrated by the human senses: Figuratively speaking, it can see, feel, hear, smell and taste events from the surrounding area. In fact, sensors are technical components that are used to measure physical, chemical and biological variables and thus make them measurable. The measured values are converted into an electrical signal and passed on to a data processing system in order to finally be evaluated.
In our online shop you will find sensors of different types as well as sensor accessories such as mounting systems and plastic housings as well as safety components, such as light barriers and safety relays.
What was the sensor?

Sensors can measure physical, chemical and biological variables. Sensors that measure physical properties include pressure sensors that can be used to determine stationary pressures, pressure differences, and pressure fluctuations, as well as motion sensors and PIR sensors typically used in motion detectors. PIR sensors only detect changes in temperature and must be distinguished from temperature sensors. A temperature sensor constantly measures the temperature, whether it changes or not. Sensors can also measure electrical parameters such as current, voltage and resistance.
Sensors for the detection of chemical quantities measure, for example, the pH value, oxygen content or the ionic strength. This grouping includes gas sensors that can be used to detect gaseous substances such as methane, ethanol, natural gas or carbon monoxide. Finally, sensors also capture biological values such as pulse, brain currents and blood pressure.
Measuring principles of sensors

Sensors operate according to different measuring or operating principles. Capacitive sensors collect data based on the change in the electrical capacity of a capacitor . Here one takes advantage of the fact that the electrical capacity of a capacitor changes with the distance of its electrodes. A measurable size can be derived from this, which can be used, for example, for distance and thickness measurement. For this reason, there are proximity switches and proximity sensors as well as distance sensors based on the capacitive measuring principle. Pressure sensors and humidity sensors that measure the moisture content of a medium can also be capacitive sensors.
In contrast to capacitive sensor technology, inductive sensor technology – as the name implies – is based on inductance. Inductive sensors operate with an alternating electromagnetic field over a copper coil, which is located in a switch core made of ferrite. If an electrically conductive metal object approaches, the magnetic field is deformed or damped. This means that the amplitude of the eddy currents in the magnetic field changes. This, in turn, causes the impedance of the coil to change. The sensor registers the change in the vibration amplitude and outputs the switching signal when a certain value is undercut. Inductive sensors are used to identify metallic or magnetic or electrically conductive objects and can be used for distance measurement. Since they measure contact-free, they play a major role in the field of automation.

Inclination sensors, which can be used to detect inclinations in the room or inclines in the environment, are sometimes based on inductive sensor technology. However, there are also capacitive inclination sensors.
Magnetic sensors have a higher range than inductive sensors and are characterized by a small design and at the same time high switching distances. They can be used universally and switch contact-free. Hall sensors (named after the American physicist Edwin Hall) are based on the magnetic measuring principle and are used to detect and measure magnetic fields.
In addition to capacitive, magnetic and inductive sensors, there are optical sensors that can detect the intensity, color and runtime of light. They consist of a light transmitter , to which the light hits, and a light receiver , which evaluates the incoming signal. Optical sensors have the advantage over capacitive, inductive and magnetic sensors that electrical or magnetic fields do not influence the measurement. They are often used in automation and smartphones.
Application areas of sensors
Sensors meet us in everyday life in many places. Radar sensors, for example, can be found in automated doors and are an essential component of radar-based parking aids . The sensors are based on radar technology: By sending out thousands of electromagnetic signals every second and measuring the time until the repeated echo, the sensor can determine the distance of a car to the environment. Ultrasonic sensors are also used in parking distance controls.
Timers and house number lighting are examples of the use of light sensors. A light sensor measures the brightness in the environment and triggers a special function if the actual value deviates from the set value. This can be, for example, switching on the light as the twilight increases. Acceleration sensors, on the other hand, measure the vibration or acceleration of an object. They are used, among other things, to deploy airbags in vehicles and in alarm systems. Acceleration sensors play a major role in technology.

Level sensors are built into coffee machines, washing machines and dishwashers to control the amount of water and warn if the water does not drain or if there is too little water in the appliance.
Sensors are also indispensable in industry. Production and logistics processes in particular are increasingly being automated, which is why the use of sensors seems inevitable. Level monitoring sensors, for example, are used to monitor rainwater tanks, compressor pressure vessels, boilers and wells or to control pumps.

Encoders detect rotational movements and are particularly useful in electrical engineering and electronics. They are used for position determination, speed measurement on rotating machines and distance measurement on conveyor belts. Sensors can also be found in chip card technology, which companies use for access control, for example.
Another large area of application is environmental technology . Sensors can be used to determine emissions in coal-fired power plants, such as carbon dioxide, and pH in sewage treatment plants or rivers. Sensors are also used to monitor drinking water, such as chlorine content.
Our practical tip: Integrate a software
The integration of software is recommended for controlling measurement projects and sensor systems as well as for the simple and fast evaluation of the recorded data. This allows, for example, thresholds or sampling intervals to be modified and data to be output in table form. Some versions even graphically prepare the data in the form of diagrams.
FAQ - Frequently Asked Questions about Sensors
What was the difference between active and passive sensors?
The distinction between active and passive sensors depends on whether or not the sensors require an electrical auxiliary power supply for the measurement. Active sensors are capable of generating voltage on their own and do not require additional external energy supply, while passive sensors do not work without auxiliary power.
Do ich need a specific switching module for each specific sensor?
Not necessarily. In our online shop you will find universal sensor modules that are compatible with many different types of sensors and sensors.