Pond pumps » The pumping specialists for your garden pond
Published: 12.08.202.1 | Reading Time: 10 minutes
This text is machine translated.
A lovingly designed garden pond in the green area in front of the company building has an inviting effect on customers, visitors and guests alike.
But employees also like to enjoy the soothing ambience of a well-tended company garden with a pond during their lunch break. Because in the often rather simply designed industrial areas, the small green oases are a welcome visual change for people and animals.
If the pond also has a gently rippling watercourse or a small fountain, the gurgling sounds of the water also contribute acoustically to a relaxing sense of well-being.
The positive additional effect: a stream or fountain naturally enriches the pond water with oxygen. Or you can use the pond pump to operate an additional filter. Then the pond inhabitants will always have optimum water quality and excellent living conditions.
In our guide, we explain how to expand your pond in the garden or on company premises with a pond pump. You will also find out what you need to bear in mind.
When we talk about pond pumps, we usually mean filter pumps or stream pumps. These pumps are ideal for operating filters or complete filter systems. However, they can also be used for a stream or waterfall. Fountain pumps also count as pond pumps and are often found in garden ponds.
To keep installation as simple as possible, most pumps for pond filters, streams or fountains are designed as submersible pumps. This means that the pumps are completely submerged in the water.
This saves you having to connect a suction line. Only the hose with the pressurized water and the power line then lead out of the pond. Fountain pumps, on the other hand, have a variably adjustable riser pipe onto which interchangeable attachments for different fountains can be fitted.
Alternatively, there are also stream or filter pumps that are operated as external pumps outside the pond. In this case, a sturdy suction hose must be fitted to the pumps to withstand the negative pressure of the water being sucked in. In addition, you must always ensure that an external pump does not run dry. This could destroy the seals and shaft bearings in the pump. In comparison, there is no such risk with a filter pump or stream pump that is operated as a submersible pump in the garden pond.
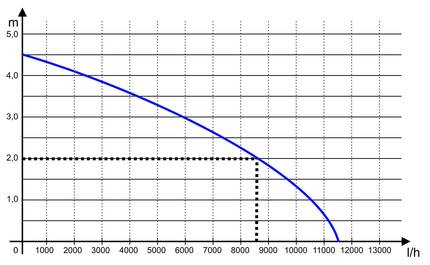
The two most important technical features of a filter pump or watercourse pump are the flow rate and the delivery head. If you look at the technical data of some pond pumps, you will see some quite impressive values. There are pumps that can deliver 11,500 liters per hour and have a maximum delivery head of 4.5 meters. However, you should not be dazzled by the figures. The pump cannot pump 11,500 liters of water 4.5 m high in one hour. Rather, the values represent maximum limit values that are only achieved when the other value is minimal.
This means that if the pump really has to pump the water 4.5 m high, the water at the outlet will only drip at most. However, if the water outlet is only slightly higher than this, the pond pump will almost reach the maximum flow rate of 11,500 l/h.
However, if you need to know exactly what the flow rate of this pump is at a delivery head of e.g. 2 m, you will need the pump characteristic curve. The characteristic curve specified by the pump manufacturer indicates exactly what flow rate can be expected at what delivery head.
According to the characteristic curve shown in the diagram, this would be approx. 8600 l/h.
In practice, however, these values are not quite achieved. The actual pump capacity depends on the flow resistance of the hose used (hose cross-section and hose length) and the flow resistance of the fittings and connectors used.
Basically, watercourse pumps are also suitable as filter pumps or filter pumps as watercourse pumps. This makes the search for a suitable pump for the pond filter much easier.
It becomes more difficult when the pump size has to be defined. The circulation rate plays an important role here. The circulation rate indicates the time period in which the entire volume of water in the pond should be pumped through the filter system.
If the circulation rate for a pond with 6000 l of water is 1 time in 2 hours, the pump must have a flow rate of 3000 l/h at the required delivery head.
The actual circulation rate required depends on the fish population, the proportion of aquatic plants, the amount of sunlight and the desired water clarity. In a fish pond with many aquatic plants, a circulation rate of once every 3 hours is perfectly adequate. In a koi pond with a high fish population and sparse planting, the circulation rate may well increase to 2 times per hour in order to achieve permanently clear water.
Important:
The pump capacity required for the circulation rate must also match the maximum filter throughput. If the pump capacity is too high, the pond filter will be flooded or will not function properly. Pressure filters can be damaged if the pressure is too high. The pond pump must also be able to pump coarse dirt and small solids. Sludge, sand or suspended matter could otherwise clog the pump so that it can no longer pump water.
As with a filter pump, the flow rate of a watercourse pump is also crucial. After all, you want a babbling brook and not a dried-up trickle. However, a mountain stream rushing down into the valley and taking all the stones and plants with it is not necessarily ideal either. The flow rate should therefore be precisely matched to the stream bed.
A rule of thumb recommends 1.5 liters of water per minute for every centimeter of width of the stream bed. For a stream with a width of 35 cm, the stream pump should have a flow rate of 3150 l/h (1.5 liters x 60 minutes x 35 cm stream width).
This flow rate must of course be possible according to the pump characteristic curve at the required delivery head. Again, the losses through the hose and the various screw connections must be taken into account.
If the calculation requires a very powerful pump, the stream can simply be made somewhat narrower and shallower. A gradient of 3 to 5% is quite sufficient. Due to the reduced water requirement and the lower delivery head, very good results can be achieved even with a lower pump capacity. If an adjustable pond pump is used, the water volume can be perfectly adapted to the stream.
Important:
Once the required pump capacity has been determined, it is important to consider the power consumption of the models in question. This is because it can make sense not to pay attention to the price, but rather to choose an energy-efficient model. The additional costs can easily be recouped later through lower electricity costs. In addition, high-quality water pumps have a particularly long service life with the right maintenance and care.
With a fountain pump or water feature pump, the height of the fountain produced is crucial in addition to the flow rate and delivery head. This is because the overall picture has to be right.
The larger the pond, the higher and more expansive the water fountains can be. However, the radius of the pond should always be larger than the height of the fountain. If the fountain is set up in the middle of the pond, the falling water cannot end up outside the pond.
Fountain pumps with an attachment for a water bell are suitable for smaller ponds. The water rising upwards is pressed against a circular baffle plate, creating a bell-shaped film of water.
Important:
When positioning the fountain pump in the pond, the plants must also be taken into account. This is because the floating leaves of pond and water lilies or floating plants, such as the mussel flower, do not tolerate being permanently wetted from above. Adjustable pond pumps are available for individual adjustment of the flow rate or the height of the fountain. To prevent coarse dirt particles from being sucked in, some fountain pumps have their own filter.
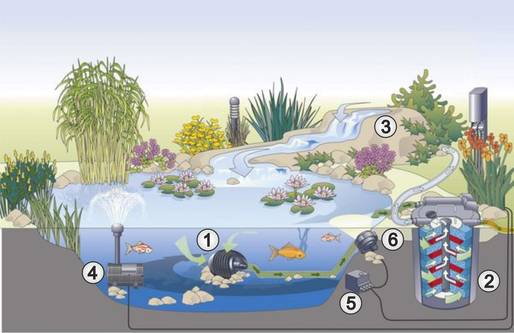
With filter pumps (1), it is important that they can circulate all the water in the pond. They are therefore installed on a flat surface at the bottom of the pond.
However, choose the location so that you can easily remove the pond pump from the water for cleaning or maintenance work.
For stream pumps, it makes sense to place the pump on a small base at the bottom of the pond. This prevents sludge or dirt from being sucked up from the bottom and carried into the stream bed. If the pump directs the water to a filter (2), it can be placed directly at the bottom of the pond.
The returning water (3) should be directed back into the pond at the greatest possible distance from the pump. If required, fountain pumps (4) provide a great water feature and additionally enrich the water with oxygen. Any planned LED underwater lighting (6) must be operated via a safety transformer (5).
Where should a filter pump be installed in the pond?
A pump should be installed at the lowest point opposite the filter inlet. This ensures optimum circulation and oxygenation of the pond water.
Can the performance of pumps be regulated?
Some pumps can be regulated mechanically to reduce the amount of water to be pumped. Some pumps can also be regulated electronically using a speed controller. However, the pump output must not exceed the maximum output of the speed controller.
Can commercially available 230 V pumps be used in swimming ponds?
No, according to VDE regulations this is not permitted. Special safety regulations apply to swimming ponds, which must be observed when installing pumps. For example, 230 V pumps must be installed in a technical shaft and plastic water pipes must be used. Alternatively, 12 V pumps can be used in the swimming pond.
Can a skimmer be connected to a pond pump?
Some pond pumps have a connection piece for a skimmer hose on the suction side. The “suction nozzle” floating on the surface then removes all solids and plant parts floating on the water surface together with the water sucked in.
Are pond pumps also suitable for solar operation?
In principle, it is possible to set up an off-grid solar system with a battery and connect an inverter with a 230 V output. However, the technical complexity is very high and also cost-intensive. For smaller ponds, special solar pumps with a solar module are available as a set or special solar watercourse pumps.
Can a pond pump also be used to operate a fountain and a water spout?
Yes, this is possible at any time. For a fountain, however, a telescopic riser pipe with an attached spray nozzle must be fitted to the pump. For a water spout, the flow rate of the pump should be adjustable in order to achieve a perfect result. Alternatively, there are also complete sets with a pump and various attachments for different fountains.
Can the pump remain in the pond over the winter?
This is only possible if the pump is installed deep enough in the pond to prevent the water from freezing. If this is not guaranteed, you should remove the pump from the pond before the first frost, clean it and store it in a bucket of water in a frost-proof place. Always follow the manufacturer's instructions in this regard.
What does the power consumption indicate?
The power consumption indicates how much power a pump requires. The value is given in watts (W). The higher the power consumption, the higher the electricity costs. If a pump with a power