Qi standard - for inductive charging
Updated: 01.08.2022 | Reading time: 9 minutes
This text is machine translated.
In principle, everything works, but without power, almost nothing works. Anyone who has ever tried to use a phone with an empty battery can confirm this. Normally this is not a problem, because you simply connect the phone to the charging cable.
After a short time, the mobile device has enough power to at least make a short call. But what if the charging cable with the corresponding power adapter is not to hand? It would be practical if the smartphone could be charged anywhere. And that's exactly what wireless charging does.
In our guide, we explain in more detail how a wireless charger works and what the Qi standard is.
There are now a wide variety of rechargeable devices in every household. Smartphones, Bluetooth headsets, watches and portable media players are all supplied with power via a charging cable.
Each device comes with a power supply unit and charging cable. You therefore need to be very careful to use the right charging cable with the right plug and the corresponding power supply unit.
With some devices, you also have to check how the micro USB plug of the charger has to be turned so that it fits into the socket. If the misaligned plug does not slide into the socket straight away, simply apply more mechanical pressure.
It is unlikely that the plug and charging socket will be able to withstand this rough treatment in the long term. Over time, the charging socket will wear out and no longer guarantee a secure connection. This will result in loose contacts and expensive repairs.
It would be better if no cable or plug contact were needed at all for charging. This is why manufacturers have developed wireless charging, which is also sometimes referred to as inductive charging.
The charging current for a smartphone, for example, cannot simply be transmitted through the air, as air is an electrical insulator for electricity. However, just as radio waves from radio or television transmitters are transmitted through the air, energy can also be transmitted. Wireless energy transmission makes use of two laws of physics:
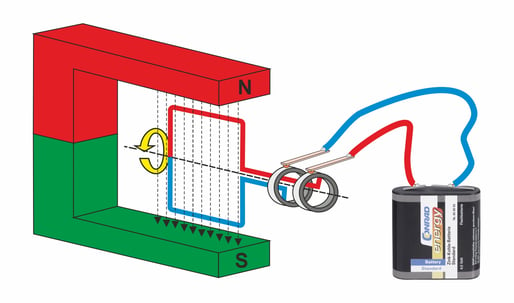
Electric motor principle
A current-carrying conductor generates a magnetic field. If the conductor is also in the magnetic field of a permanent magnet, the two magnetic fields influence each other and the rotary motion of an electric motor is created.
Generator principle
When an electrical conductor moves in a magnetic field, an electrical voltage is generated (induced) in the conductor. The functional principle of this current generation is used in generators or dynamos.
Combination of both basic principles
In practice, two coils are used for inductive charging. One coil is the transmitting coil and the other coil is the receiving coil. The transmitter coil builds up the required magnetic field. In order for the receiving coil to generate (induce) a voltage, it would have to move in the magnetic field. As this is not mechanically possible, a trick is used. Instead of moving the conductor of the receiving coil, the magnetic field is moved. This is achieved by operating the transmitting coil with alternating voltage. The resulting constantly changing magnetic field then also generates an alternating voltage in the receiving coil, although the receiving coil itself is not moved.
In technology, this principle has long been used in transformers. The only difference is that in transformers, the magnetic field between the two coils is amplified by a core of iron plates and conducted in a targeted manner. This means that a transformer can also transmit high power in some cases.
With inductive charging, however, the reinforcing effect of the iron core is missing. It is therefore important that the two coils are very close to each other. The distance should be as small as possible. Only then can energy be transferred efficiently. However, even under ideal conditions, the transferable power of inductive chargers is only a few watts. However, this power is quite sufficient for charging small personal wearables (portable electronic devices).
As clever as the idea of inductive charging of mobile devices is, the technical implementation is complicated. This is because there were and still are technical difficulties that need to be overcome during implementation.
The functionality must be given
The most important point is probably the functionality.
It must be ensured that sufficient energy reaches the receiver (smartphone) so that the battery is charged with sufficient current.
In addition to the aforementioned minimum distance between the coils, the strength of the magnetic field and the frequency of the AC voltage can also be influenced by the charger manufacturer.
Ideally, the transmitter and receiver should be perfectly matched.
Safety must be guaranteed
The charging process may only be started when the corresponding phone is resting on the transmitter coil. In addition, the magnetic field must not interfere with any other devices in the immediate vicinity during charging.
If foreign objects such as a paper clip, jewelry, tools or a nail file accidentally come into contact with the transmitter coil of the charging station, the charging station must not be started.
This is because the induced currents within the metal parts would cause the objects to heat up to such an extent that they could burn you.
Compatibility must be ensured
When it comes to technical innovations, it is often standard for each manufacturer to go their own way when implementing a wireless charger. It is therefore very easy for the inductive charging process to fail or not work properly if the charging station and the smartphone are not from the same manufacturer. In the worst case scenario, the receiver coil in the cell phone induces a voltage that is far too high, causing damage to the smartphone.
Especially when a wireless charging device is provided in public facilities, you need to be sure that the smartphone charges quickly but is not damaged by the charging process. This is why the Wireless Power Consortium developed the Qi standard.
The WPC (Wireless Power Consortium) is a non-profit organization founded in 2008 with more than 650 member companies from all over the world. Leading brands such as Apple, Samsung, Huawei, Xiaomi, Google, LG, Sony, Nokia and many other manufacturers have joined the WPC.
Together with its members, the WPC develops cross-manufacturer standards for wireless power supply.
Qi (pronounced “chi”) stands for vital energy or life force in Chinese. In connection with charging technology, Qi is the world's leading standard for inductive charging with an output of up to 15 W. The Qi standard not only describes the functional aspects of inductive charging or a QI charger. Safety-relevant protective devices and reliable foreign object detection have also been precisely defined in the QI standard. Another Qi specification describes the magnetic shielding of the battery to minimize heating during wireless charging.
Manufacturers of inductive smartphone chargers can apply to the WPC for certification for their wireless chargers. To this end, authorized and independent test laboratories test the chargers to determine the extent to which the wireless chargers meet the strict requirements of the Qi standard. The product-specific properties in terms of safety, interoperability and user-friendliness are tested in detail. If the wireless charger fully complies with all the requirements of the Qi standard, the charging station may bear the Qi logo as a Qi-certified product. This ensures that all Qi-certified products are compatible with each other and work perfectly together wirelessly. Users can safely place their Qi-enabled smartphone on any Qi-certified charger without having to worry about damaging the phone on the charging station.
At the moment, the Qi standard is still primarily used for charging smartphones. However, the members of the WPC are working hard to increase the power profile for the Qi standard. Devices such as laptops and tablet PCs with a charging power of 30 to 60 W can then also be covered.
If you want to know whether the inductive charger you are using has Qi certification, you can check the Wireless Power Consortium database.
In close cooperation with the manufacturers and the Wireless Power Consortium, Conrad Electronic has decided to only include Qi-certified chargers for wireless charging in its product range.
This gives our customers the absolute certainty that a Qi-certified smartphone will work with the Qi charger without any problems. The smartphone is optimally charged and all safety-relevant aspects are also taken into account. This always gives our customers and us a good feeling when it comes to wireless charging.
Wireless and safe charging of cell phone batteries with Qi technology is currently just the tip of the iceberg. Wired chargers or charging stations with micro-USB cables will probably be completely replaced by wireless chargers sooner or later. Wireless Qi chargers offer the best conditions for this.
But wireless charging has even more potential. For example, in the future it will no longer be necessary to connect blenders, toasters and the like to a power socket using a mains cable. The appliances will be wireless and equipped with intelligent charging technology (Standard Ki Cordless Kitchen). You simply place them on a marker on the work surface and they are then powered by induction.
Wireless charging is also a development requirement for electric cars and e-bikes. However, as much higher power has to be transmitted here, the technical implementation will probably take some time. Nevertheless, wireless charging with Qi charging technology will become increasingly standard in the near future.
How do I know if my cell phone is suitable for a Qi charger?
If in doubt, you should check the manufacturer's website or the product data sheet to find out whether the cell phone can be charged wirelessly with a Qi charger. If this is not possible, you can find overviews on various websites that list all cell phones that can be operated wirelessly on a Qi charger.
Can I charge a Qi-enabled cell phone on any wireless charger?
This is only possible if the wireless charger also supports the QI standard. If the wireless charging station or wireless charger does not support the Qi standard, charging is not recommended.
What can I do if my cell phone is not Qi-enabled?
Some manufacturers now offer Qi retrofit kits for certain mobile devices. These Qi receivers are simply connected to the charging socket of the cell phone and attached to the back. In some cases, it is also possible to place the narrow receiver between the cell phone and the protective cover. However, this may cause problems with wireless charging.
Does wireless charging also have disadvantages?
There are also some minor disadvantages to wireless charging. As wireless energy transfer is not as efficient as a charging cable, the charging process takes significantly longer. In addition, the cell phone has to rest on the charging cradle and therefore cannot be used or can only be used to a very limited extent.